Table of Contents
- 1. Introduction
- 2. Understanding Post-Stroke Balance Challenges
- 3. Professional Balance Rehabilitation Approaches
- 4. Essential Balance Improvement Exercises
- 5. Assistive Devices and Balance Support Tools
- 6. Home Safety and Environment Modifications
- 7. Psychological Aspects of Balance Recovery
- 8. Advanced Balance Recovery Technologies
- 9. Nutrition and Lifestyle for Balance Recovery
- 10. Conclusion
- 11. Call to Action
- 13. Newsletter Signup:
- You May Also Be Interested In:
1. Introduction
Balance is a crucial aspect of recovery after a stroke, directly impacting a person’s ability to move safely and independently. Stroke can significantly affect balance, making rehabilitation essential. With targeted exercises and the right strategies, stroke survivors can improve their balance, regain stability, and enhance their quality of life. This journey requires persistence, but the potential for improvement is substantial.
2. Understanding Post-Stroke Balance Challenges
2.1 Neurological Impacts on Balance
- How Stroke Affects the Vestibular System: The vestibular system in the inner ear helps control balance. A stroke can disrupt this system, leading to balance issues.
- Brain’s Role in Maintaining Balance: The brain integrates sensory information to maintain balance. Stroke can impair these neurological connections, affecting balance.
- Neurological Connections and Movement: Stroke disrupts the brain’s ability to coordinate movement and maintain balance.
- Types of Balance Impairments: Includes difficulties with static (standing still) and dynamic (moving) balance.
2.2 Common Balance Disruption Mechanisms
- Muscle Weakness: Stroke often results in muscle weakness, making it difficult to maintain balance.
- Sensory Processing Challenges: Sensory deficits can impact the ability to perceive spatial orientation.
- Proprioception Difficulties: Stroke can affect proprioception, the sense of body position and movement.
- Coordination and Motor Control Issues: Difficulty coordinating movements can lead to balance problems.

3. Professional Balance Rehabilitation Approaches
3.1 Physical Therapy Interventions
- Comprehensive Balance Assessment: Physical therapists assess balance to identify specific issues and tailor rehabilitation plans.
- Personalized Rehabilitation Strategies: Developing individualized plans that address unique balance challenges.
- Progressive Balance Training: Gradually increasing the complexity of balance exercises to improve stability.
- Multidisciplinary Recovery Approach: Collaborating with other healthcare professionals for comprehensive care.
3.2 Specialized Balance Recovery Techniques
- Proprioceptive Neuromuscular Facilitation: Techniques that enhance proprioceptive feedback to improve balance.
- Vestibular Rehabilitation: Exercises that target the vestibular system to improve balance.
- Sensory Integration Training: Methods that enhance sensory processing and integration.
- Adaptive Balance Improvement Methods: Customized approaches to address specific balance impairments.
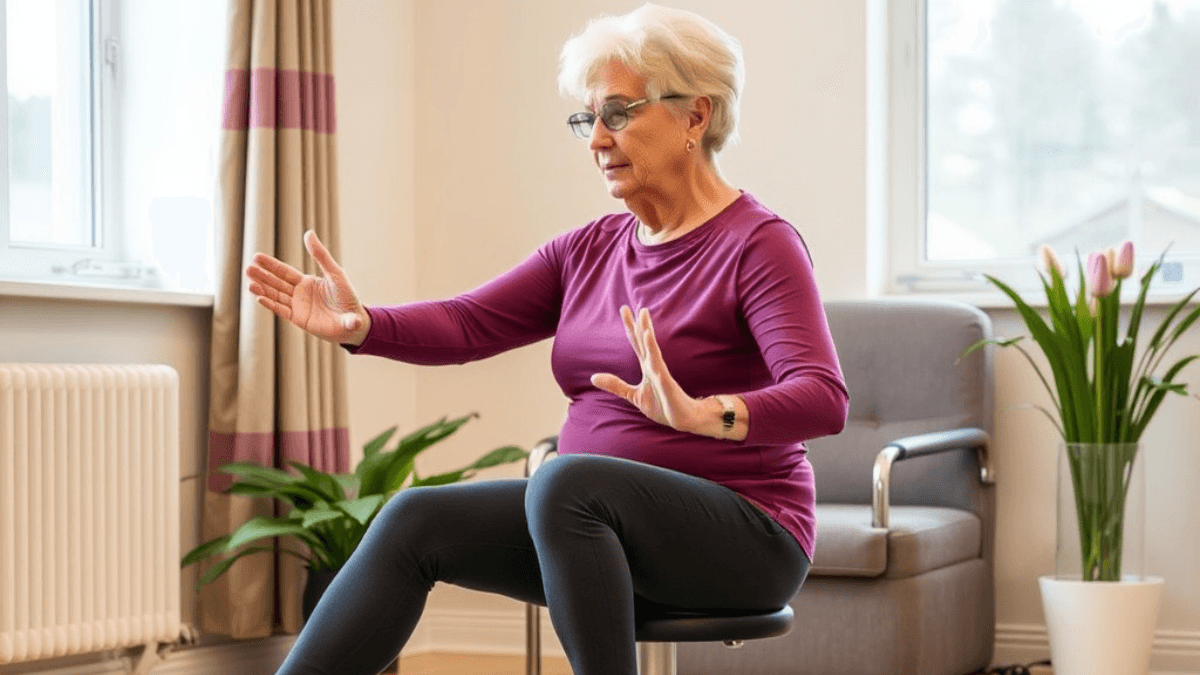
4. Essential Balance Improvement Exercises
4.1 Core Strengthening Techniques
- Seated Balance Exercises: Activities that improve balance while seated, such as reaching and bending.
- Standing Balance Drills: Exercises performed while standing to improve stability.
- Weight Shift Practices: Shifting weight from one foot to the other to enhance balance.
- Stabilization Techniques: Techniques that focus on core stability to support overall balance.

4.2 Specific Balance Recovery Exercises
- Single-Leg Standing: Standing on one leg to improve balance and strength.
- Controlled Movement Patterns: Exercises that involve slow, controlled movements to enhance coordination.
- Eye-Tracking Balance Exercises: Movements that combine eye and head movements to improve balance.
- Walking and Turning Techniques: Practicing walking and turning to improve dynamic balance.
5. Assistive Devices and Balance Support Tools
- Types of Balance Assistance Devices: Canes, walkers, and balance trainers.
- Selecting Appropriate Walking Aids: Choosing the right device based on individual needs and abilities.
- Adaptive Balance Technologies: Innovative tools that support balance recovery.
- Home Safety Equipment: Devices that enhance safety at home.
- Amazon Affiliate Product Recommendations: Suggested products available on Amazon to aid balance recovery.
6. Home Safety and Environment Modifications
6.1 Creating a Safe Living Space
- Fall Prevention Strategies: Methods to reduce the risk of falls.
- Home Layout Adaptations: Arranging furniture to create clear pathways.
- Support Rail Installations: Installing rails in key areas for support.
- Removing Potential Hazards: Ensuring the home environment is free of obstacles.
6.2 Adaptive Home Strategies
- Flooring Considerations: Using non-slip flooring materials.
- Lighting Improvements: Ensuring adequate lighting to prevent falls.
- Furniture Arrangement: Placing furniture to allow easy movement.
- Mobility-Friendly Design Principles: Designing the home to support mobility and balance.

7. Psychological Aspects of Balance Recovery
7.1 Mental Resilience and Motivation
- Overcoming Fear of Falling: Building confidence to reduce fear of falling.
- Building Confidence: Encouraging self-belief and perseverance.
- Setting Realistic Recovery Goals: Establishing achievable milestones to motivate progress.
- Maintaining Positive Mindset: Fostering a positive outlook on recovery.
7.2 Emotional Support Strategies
- Dealing with Frustration: Techniques to manage frustration during recovery.
- Family Support Techniques: Encouraging family involvement and support.
- Counseling Resources: Accessing professional mental health support.
- Support Group Participation: Joining support groups for shared experiences and encouragement.
8. Advanced Balance Recovery Technologies
8.1 Cutting-Edge Rehabilitation Methods
- Virtual Reality Balance Training: Using VR to simulate balance exercises.
- Electrical Stimulation Techniques: Using electrical impulses to stimulate muscle activity.
- Biofeedback Technologies: Providing real-time feedback to improve balance.
- Neuroplasticity-Focused Interventions: Exercises that enhance brain plasticity.

8.2 Emerging Rehabilitation Tools
- Wearable Balance Support Devices: Devices designed to support and enhance balance.
- Smart Tracking Technologies: Advanced tools for tracking and monitoring progress.
- Digital Progress Monitoring: Using digital tools to track recovery.
- Adaptive Rehabilitation Systems: Innovative systems to support balance recovery.
9. Nutrition and Lifestyle for Balance Recovery
- Diet Supporting Neurological Healing: Consuming a brain-healthy diet to support recovery.
- Exercise and Physical Activity Guidelines: Following recommended exercise routines.
- Sleep and Recovery Relationship: Understanding the importance of sleep in recovery.
- Stress Management Techniques: Techniques to manage stress effectively.
10. Conclusion
Improving balance after a stroke requires a combination of physical therapy, consistent practice, and psychological support. Persistence and the right strategies can lead to significant improvements in stability and confidence. Stroke survivors should remain hopeful and committed to their recovery journey.
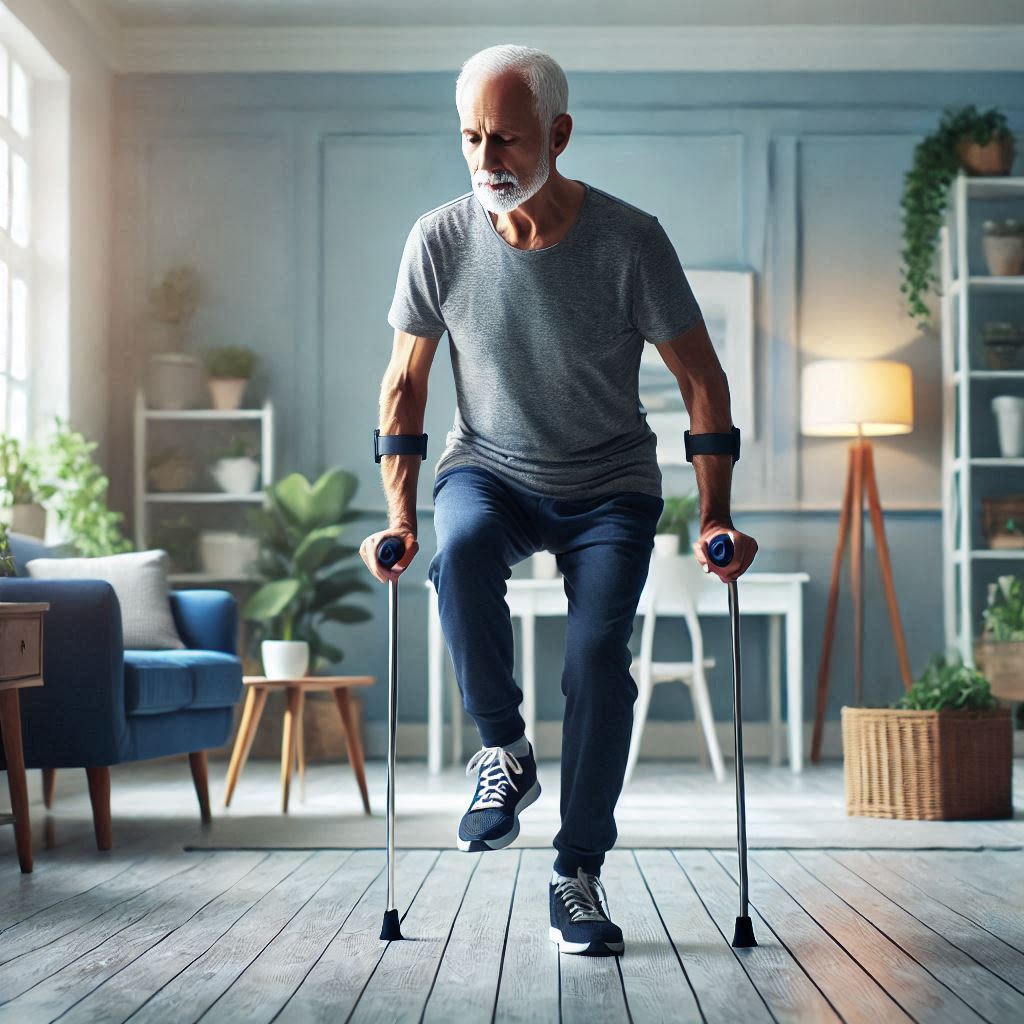

11. Call to Action
We encourage you to share your experiences and tips in the comments section. Explore our website for more resources and product reviews to aid in your balance recovery journey. Engage with our community for support and stay informed with the latest tips and tools to enhance your recovery process.
13. Newsletter Signup:
- Empowering Recovery: Get the latest tips, knowledge, products, and blogs to support your stroke recovery journey.
- Stay Informed: Receive expert advice, inspiring stories, and practical resources for a successful stroke recovery.
- Join Our Community: Subscribe to access valuable insights, helpful products, and support for stroke survivors.
Categorie
Recent Post
- Financial Effects of Stroke: Managing Costs and Finding Support
- Improving Balance After a Stroke: Tips and Exercises for Stability
- Improving Arm and Hand Function After a Stroke: Rehabilitation Techniques
Popular Products






Leave a Reply